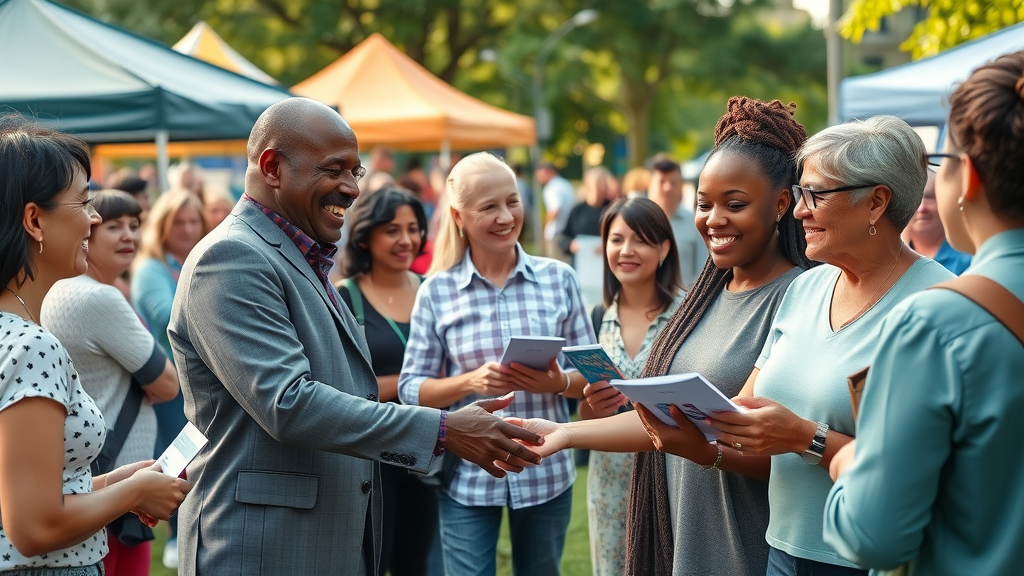
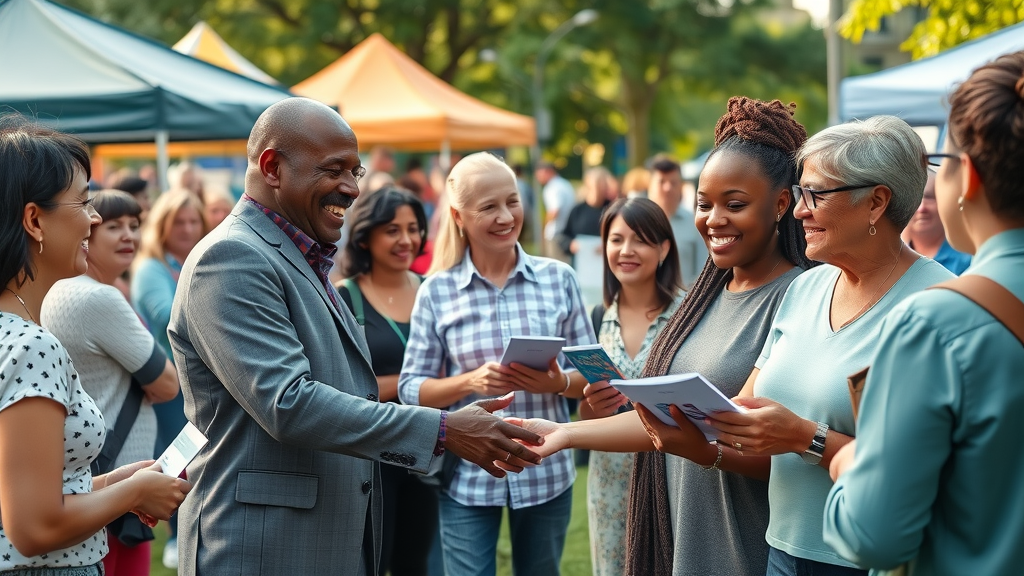
Did you know that over 70% of community outreach programs result in measurable improvements in local public health, education, and economic opportunity? Imagine your neighborhood blossoming because of a single project, transforming lives and igniting momentum for years to come. In this comprehensive guide, you’ll discover how community outreach programs can spark real, sustainable change and learn the actionable steps to build or improve your own outreach initiatives. How Community Outreach Programs Transform Local Communities Community outreach programs serve as powerful catalysts for change by addressing the unique needs of neighborhoods and empowering individuals. These programs connect community leaders , local businesses, volunteers, and citizens to foster community engagement and resilience. For example, an educational workshop held at a community center might boost literacy rates among school students , while a food drive could provide essential services to hundreds of families in need. By working hand in hand with community members , outreach initiatives build trust and inspire people to get involved. This sense of ownership and collective responsibility is the foundation for lasting impact. Local events—such as community fairs , health screenings, or cultural festivals—act as dynamic spaces for residents to connect, share resources, and celebrate local culture , deepening the sense of belonging and pride within the local community . Startling Statistics: The Measurable Reach of Effective Community Outreach Programs The positive outcomes of community outreach programs are tangible and far-reaching. Reports show that communities with robust outreach efforts report up to 30% higher rates of community involvement and volunteerism. Additionally, neighborhoods with established outreach programs experience reduced crime rates, lower unemployment, and stronger ties between diverse community groups . These figures underscore how strategic investments in outreach initiatives spark real positive change. In educational outreach programs, for instance, high school students participating in after-school tutoring see significant improvements in graduation rates. Similarly, mental health awareness campaigns have led to increased resource utilization, reducing stigma and ensuring timely support for individuals and families. The ripple effect of a well-supported community outreach program is undeniable: it creates healthier, more vibrant communities prepared to tackle future challenges. Community members and leaders coming together at a local outreach event. Key Benefits of Community Outreach Programs in Driving Positive Change Participation in community outreach programs offers a wealth of advantages for both individuals and neighborhoods. These initiatives empower local leaders, foster deeper community engagement , and stimulate collaboration between various groups, including local businesses and service providers. For marginalized populations, outreach programs are a lifeline to resources that might otherwise be inaccessible. Moreover, outreach programs break down barriers between organizations and residents, nurturing a sense of trust and partnership. When communities band together to address shared challenges or celebrate achievements, they cultivate a sense of belonging and mutual support—critical ingredients for sustainable growth and resilience. Empowerment of community leaders Enhanced community engagement Resource sharing through local businesses Uplifting marginalized populations Understanding Community Outreach: What Are Community Outreach Programs? At their core, community outreach programs are organized efforts by groups such as nonprofits, local government, businesses, and volunteer networks to bring support and resources directly to individuals and families. These outreach initiatives are designed to respond to the most urgent needs in the community—be it food security, access to healthcare, education, or cultural development. This approach positions community outreach programs as essential bridges between community organizations and those they serve. Programs might range from providing meals to the homeless, hosting educational workshops , to organizing events that promote healthy relationships and mental health awareness. No matter the focus, all great outreach programs share a foundational commitment to listening, responding, and building lasting trust with the local community . Defining Community Outreach Programs and Their Core Objectives "Community outreach programs create critical bridges between organizations and the people they serve." The principal goal of any community outreach program is to improve quality of life—for individuals and for the collective. Outreach initiatives strive to: Provide resources to underserved or vulnerable groups Promote education, wellness, and socioeconomic mobility Build a sense of community and foster strong connections among residents Facilitate access to essential services such as healthcare, food distribution, and counseling Whether through one-time events or ongoing programming, the core mission remains the same: meet people where they are and deliver meaningful, transformative support. Volunteers and nonprofit leaders collaborating at a modern community center. Building Blocks: Major Types of Community Outreach Programs The structure of community outreach programs varies widely to address local priorities and community interests. Some focus on immediate needs, like food or housing, while others center on long-term improvement, such as education , job training, or mental health support. Recognizing which type of outreach program will yield the greatest impact is crucial for organizations or individuals launching a new initiative. Ultimately, it's this adaptability and purposeful design that allow outreach efforts to address evolving challenges and foster interconnected, resilient neighborhoods. Outreach Initiatives: Educational, Health, and Social Assistance Programs Educational outreach programs, like after-school tutoring or adult literacy classes, equip community members with new skills for brighter futures. Health outreach programs—think mobile clinics, vaccination drives, or mental health workshops—ensure every resident can access support, regardless of background. Social assistance programs play a vital role by directly providing food, shelter, or legal aid to those facing hardship. These outreach initiatives are particularly important in underserved areas, where barriers to education, healthcare, or basic needs are often greatest. Over time, such focused programs have been shown to significantly improve public health, increase high school graduation rates, and help entire families move toward economic stability. Healthcare professionals conducting free screenings at a local outreach event. How Local Events and Volunteer Projects Strengthen Community Engagement Local events and volunteer-driven projects are cornerstones of successful community outreach programs . Activities like neighborhood cleanups, public lectures, holiday festivals, or organizing a community garden not only address pressing local issues—they also unite diverse residents and provide practical opportunities for community action . By volunteering at a soup kitchen or helping coordinate a community fair , individuals discover new ways to give back and take pride in their unique contributions. Over time, these events strengthen community engagement and lay the groundwork for healthy relationships between all groups involved—residents, community organizations , local businesses , and government agencies. Overview of Common Community Outreach Program Types: Type Purpose Example Educational Outreach Improve literacy, job skills Adult classes Health Outreach Support healthy lifestyles, screenings Free clinics Social Assistance Program Provide resources to vulnerable groups Food drives Local Events/Engagement Bring people together, foster relationships Community fairs Planning Successful Community Outreach Programs: A Step-By-Step Guide Crafting an effective community outreach program requires thoughtful planning, deep local insight, and a willingness to adapt. Begin by identifying the most pressing needs in your neighborhood through surveys, interviews, or focus groups. Set measurable goals—such as “increase parental participation in local events by 25%” or “distribute 1,000 books to school students annually”—to guide your outreach initiatives and assess progress. Involve community leaders and stakeholders early. Collaboration with local businesses and established community groups can leverage unique resources, networks, and expertise. Finally, design outreach activities that are culturally relevant and accessible, ensuring everyone can participate. Setting Measurable Goals for Outreach Programs When launching or refining your community outreach program , clarity is key. Define what success looks like for your group: Are you trying to reduce food insecurity by a certain percent, increase community garden volunteers, or see more children attending after-school programs? Set both short- and long-term objectives and use specific, quantifiable metrics, such as attendance numbers, distributed resources, or follow-up survey results. These clear benchmarks allow outreach program organizers and volunteers to track progress, make data-driven decisions, and celebrate milestones along the way, encouraging ongoing community involvement and deeper engagement. Engaging Community Leaders and Local Businesses Community leaders bring deep local knowledge and trusted relationships to any outreach effort, making them invaluable allies. Meanwhile, local businesses can provide sponsorship, materials, venues, or volunteers. Building these partnerships ensures that outreach initiatives have broad community buy-in and can access critical resources quickly when needs arise. Consider forming advisory committees with business owners, educators, and health professionals, or co-hosting local events at popular gathering spots. Recognize contributions from these stakeholders, and nurture ongoing dialogue to strengthen collective impact. Community leaders and local businesses strategizing for a new outreach program. Promoting Outreach Initiatives through Local Events Use local events —like resource fairs, free health screenings, or festivals—to raise awareness and invite participation. These occasions provide a natural platform for recruiting new volunteers, sharing success stories, and showcasing how outreach efforts create meaningful change in the local community . Consider leveraging digital communication too: publicize your events through email newsletters, social media, and online community calendars to broaden your outreach and ensure maximum turnout. Measuring Impact: How to Evaluate Community Outreach Program Success The real test of a community outreach program comes when you pause to measure its impact. Successful programs use surveys, interviews, and direct data collection to track outcomes. This could mean measuring the number of families served at a food pantry, increases in community engagement , or shifts in public health metrics after a mental health awareness campaign. Don’t overlook the value of gathering testimonials and personal stories from beneficiaries and volunteers alike—these narratives help personalize your outreach’s value, drive support, and reveal new avenues for improvement. Tracking Outcomes and Gathering Testimonials for Outreach Programs Actively collect data at every stage of your community outreach program . This could mean distributing surveys after an educational workshop, keeping attendance logs at local events, and recording how often particular services are used. In parallel, ask program participants to share their experiences—a brief quote or longer video testimonial. These insights are crucial for fundraising, reporting to stakeholders, and making continuous improvements to your outreach initiatives. By sharing stories from both community leaders and recipients, you give a human face to your impact. Program recipients sharing their transformation stories through video testimonials. Adjusting Outreach Initiatives for Greater Positive Change "Lasting change in any community is built on the persistent efforts and adaptability of outreach programs." – Nonprofit Leader The most impactful community outreach programs embrace ongoing learning. Analyze your results and remain open to change: if a food drive is successful but literacy sessions have low attendance, consult with community members to investigate causes. Adjust event times, locations, or promotional strategies until you see improvements. Regularly check in with volunteers, residents, and organizational partners to ensure the outreach program remains aligned with local needs. This feedback-driven approach guarantees that outreach efforts continue to create positive change year after year. Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Successful Community Outreach Programs Across the country, community outreach programs are making a difference in countless ways, from food access and public health to education and social integration. These case studies offer practical inspiration for anyone seeking to drive positive change in their own neighborhood. When grassroots organizations teamed up with local school students for “Read Across Our Neighborhood Week,” book donations surged by 500%, and every child in the district received age-appropriate reading materials. Meanwhile, at a summer health fair launched in partnership with local businesses , hundreds of families participated in wellness screenings and mental health workshops, resulting in doubled community clinic registrations and increased engagement with ongoing services. How Local Events Drove Community Engagement and Positive Change One successful example comes from a city’s annual “Clean and Green” initiative—where community leaders organized a month-long series of cleanups, recycling drives, and planting days at a local park and community garden. Participation from residents, business owners, and students not only beautified the local area but also fostered genuine relationships and instilled environmental awareness in younger generations. Likewise, a multicultural arts and music festival introduced to celebrate local culture drew participants from across neighborhoods, strengthening cross-cultural ties and increasing attendance at future outreach events, ultimately building stronger community bonds. Assistance Programs that Built Stronger Community Ties The “Warm Meals, Open Hearts” social assistance program, managed by a network of volunteer cooks and drivers, delivered thousands of hot meals to homebound seniors each winter, significantly reducing feelings of isolation and improving recipients’ sense of belonging. This initiative simultaneously provided high school students with meaningful volunteer experience and encouraged local grocers to support community action through food donations. Another model came from a rural area where the launch of a community garden brought together residents from all walks of life. This initiative yielded fresh produce for food pantries, educational workshops for children and families, and a new gathering space for neighborhood events—fostering healthy relationships, teamwork, and resource sharing. Top 5 Community Outreach Programs That Transformed Local Communities: Community Garden Initiatives Neighborhood Clean Up Drives School Supply Assistance Programs Free Health Screening Clinics Cultural and Arts Festivals Expert Advice from Community Leaders on Sustaining Outreach Programs "Community outreach is not a one-time initiative—it is a sustained, evolving partnership between organizations and local residents." – Community Leader Veteran community leaders agree: success in outreach is about long-term vision and adaptability. Prioritize the creation of open feedback loops with program participants and fellow organizers. Don’t be afraid to pilot new outreach initiatives , adjust your approach, and celebrate wins publicly to maintain teamwork and enthusiasm. Mentorship from established community leaders and support from local businesses can provide continuity and extra hands when needed, ensuring your outreach program weathers challenges, maintains relevance, and ignites positive change over generations. People Also Ask What is a community outreach program? A community outreach program is an organized effort by nonprofits, businesses, or government groups to provide information, services, or resources directly to residents. These programs address specific needs—such as health, education, social services—strengthen community engagement , and aim to create positive change in the local community . What is an example of a community outreach activity? An example would be hosting a free health clinic where medical professionals offer screenings, vaccinations, and wellness information to residents of a neighborhood. Other activities include food drives, educational workshops, mental health support sessions, or organizing a neighborhood clean-up event—all designed to foster community involvement and address pressing needs. What is an example of a community programme? Community programs can range from an after-school tutoring service for high school students to a community garden project where residents grow fresh produce together. Each aims to bring people together, share resources, and solve local challenges collaboratively. What is community outreach work? Community outreach work encompasses the planning and execution of programs that address local needs. This can mean connecting individuals and families with vital resources, organizing events, or bringing together diverse community groups for positive action and support. Frequently Asked Questions about Community Outreach Programs How do I start a community outreach program? Begin by identifying a specific community need, gathering a team of committed volunteers or partners, and setting clear goals. Seek input from community leaders and residents, design accessible outreach activities, and measure progress as you go. What resources can assist community outreach leaders? Leverage local nonprofit associations, grant opportunities, crowdfunding campaigns, and partnerships with local businesses . Public libraries, government agencies, and online networks also offer invaluable tools and support. How do outreach initiatives lead to positive change? Outreach initiatives foster positive change by directly addressing local needs, connecting residents, and empowering individuals to act. Over time, they build healthier, more cohesive communities and set the stage for long-term improvement. What are the best metrics for measuring outreach success? Track quantitative data (attendance, resources distributed) and qualitative feedback (beneficiary testimonials, volunteer satisfaction). Assess ongoing needs and adjust your outreach program accordingly for greater impact. Young leaders planning innovative community outreach initiatives for local impact. Key Insights for Sustained Impact with Community Outreach Programs Achieving lasting change requires consistency and innovation. Regular community engagement ensures that outreach initiatives remain relevant and impactful. By forming sustained partnerships with community leaders , residents, and local businesses , and keeping programs flexible, your outreach efforts will continue to meet evolving challenges and capture emerging opportunities. Actively cultivating feedback, celebrating small victories, and updating your strategies regularly are key to maintaining momentum and delivering real benefits to individuals and families year after year. Consistent Community Engagement as the Foundation of Lasting Outreach The most successful community outreach programs are those built on continual interaction, trust, and a culture of service. Keep doors open for dialogue, encourage ongoing volunteerism, and adapt programs in partnership with the local community. This consistency builds a resilient, unified environment where every member feels valued and empowered. Above all, remember that effective outreach is not a one-time event, but a continuous cycle of learning, engaging, and growing alongside those you serve. Taking Action: Start Your Community Outreach Program Today to Ignite Positive Change Now is the perfect time to join the movement. Start by reaching out to community leaders , joining a volunteer project, or launching a new initiative to meet a local need. Every act of outreach—no matter how small—multiplies hope and creates ripples of positive change in your local community! To deepen your understanding of effective community outreach programs, consider exploring the following resources: “Six Community Outreach Programs You Should Know About” : This article highlights impactful initiatives like Meals on Wheels and the Boys & Girls Clubs of America, showcasing diverse approaches to community engagement. ( theupsstore.com ) “Discover Outreach Programs for Community Growth” : This piece outlines seven examples of community outreach programs, including health clinics and job training workshops, emphasizing their role in building stronger communities. ( famessentials.org ) If you’re serious about enhancing your community outreach efforts, these resources offer valuable insights and practical examples to guide your initiatives.




 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment